One of the most underrated components the computer power supply can and will fail over time in both laptop computers and desktop. Power Supply or PSU are one of the most common points of failure. Today we are going to discuss how to identify power supply failure quickly so it can be addressed and corrected as painlessly as possible. Secondly we are going to discuss how to identify a suitable PSU for replacement.
Signs of power supply failure
The following symptoms are indicative of power supply failure
-
When it comes to PC repairs, there are a variety of issues that can arise, such as power-on fails, continuous rebooting, excessively hot power supply, grounding on the case causing shock when touched, and intermittent hangs/freezes. Power-on fails occur when the system fails to start or experiences lockups, which can be caused by a range of factors including hardware failures or software issues. Continuous rebooting is another common problem that may indicate problems with the operating system or hardware components. An excessively hot power supply can lead to overheating and potential damage to other components within the computer. In some cases, the PSU grounding on the case could result in electric shocks when touched, posing a safety hazard for users. Lastly, if a computer is dead with no LED lit on the motherboard or experiences intermittent hangs/freezes while running, it could signal underlying hardware malfunctions that require immediate attention from professional technicians specializing in PC repairs.
How to diagnose a failing Power Supply
As part of any maintenance schedule on a computer the voltage levels on the 12, 5 and 3.3 volt rails should be assessed. This technique will also allow you to diagnose the power supply.
The power supply delivers 12 , 5 and 3.3 volts to the PC motherboard , cpu, drives and graphics. The picture below is from software called Hardware Monitor which is free and available from https://www.cpuid.com/softwares/hwmonitor.html
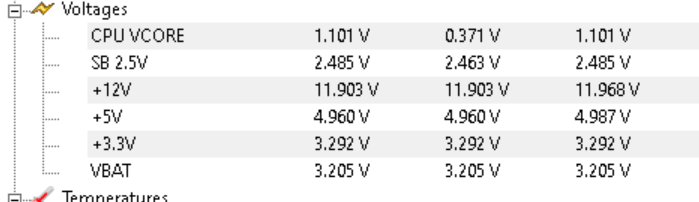
Power Supply Tester
Another method of diagnosing a PSU is to use a power supply tester

Once you have identified the power supply as the source of the pc repair problem should always replace it . Never attempt to open or repair a power supply as they contain high voltage capacitors which retain charge.
How to select a Replacement Power Supply
More complex systems require more power to run. A gaming computer with custom liquid cooling a high-end cpu, and and a top end graphics card is going to need a higher wattage computer power supply.
To recommend a power supply we need to get a ballpark figure of how much power it will consume. Using a a power supply calculator, will allow us to calculate this figure of how many watts you will need.
As a rule of thumb allowing a PSU to run at 50% of it’s maximum power is optimal. this not only protects the power supply but will ensure the longevity of your expensive components. You also need to consider the peak power supply which can be way higher when specific games or machine learning calculations are occurring. If cost is a factor then apply this rule lf your system is going to use 500 watts (a common number for a straightforward gaming build), choosing a PSU with 600 or 650-watt output could be a good option, as it will give you some overhead to work with, and also allow for potential future upgrades.
When considering a higher wattage power supply unit, don’t forget that it won’t consume more energy just because it can output more – in fact, your system will only consume as much as it requires. Therefore, selecting a feature-rich PSU with adequate wattage and high efficiency should be your number one priority over buying something much higher than you need.
In addition to your new PSU’s continuous power capabilities it’s peak power capabilities should also be considered. A PSU’s peak power is the maximum amount of power it can deliver for a short period of time, whereas its continuous power is the amount of power it should deliver on a regular basis. When you run demanding games or if you running hardware benchmarks, your system will probably consume aound it’s peak power.
If there is a sudden demand for more power, your PSU should be able to handle the higher output briefly, but should not be expected to run at those higher wattages continuously. Don’t choose the PSU solely based on peak power capabilities; make sure it has sufficient continuous power output.
Providing protection
It is important that a power supply has fail-safes built in: not only to protect the power supply itself, but also to enable protection of your expensive internal components in case of an unexpected power surge.
As the PSU occupies a unique position in the PC layout, making sure it has built-in protection can also help protect the rest of your hardware. You only have direct connections to almost all other pieces of hardware in your system through the power supply and the motherboard
Check to see that the power supply you’re looking at has built-in protection, such as OVP (Over Voltage Protection), which shuts down the power supply when excessive voltage is detected. In addition you can also get short circuit protection which can mitigate effects from power fluctuations and is a highly recommended safety feature.
A surge protector or an Uninterruptable Power Supply will also help protect your PC by diverting any potentially damaging power surges away from your valuable components
For more information about computer repair services offered click on the link.

